About Me
Hi! I'm Daksh, a graduate student at the Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, where I'm pursuing a Master of Science in Robotics Systems Development. I previously earned my Bachelor of Technology in Engineering Physics from the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati.
I'm interested in building intelligent robotic systems that can safely and reliably interact with the human world. I enjoy working at the intersection of learning, control, and real-time perception, with a particular focus on medical and biomimetic robotics.
I’m currently an AI Resident at 1X, working on reinforcement learning for the NEO Gamma humanoid. Previously, I collaborated with Dr. S. M. Hazarika at IIT Guwahati and Dr. Nithin V. George at IIT Gandhinagar.
In my spare time, I’m usually playing Minecraft, watching cooking videos (then ordering DoorDash :P), or sleeping.

News
Successfully demonstrated our MRSD Capstone project to both CMU and Smith & Nephew.
Finished in 3rd place in the CMU VLA Challenge and presented our work at IROS 2025!
Completed my summer internship at 1X, focusing on Reinforcement Learning.
Started graduate school at CMU's Robotics Institute!
Graduated from IIT Guwahati with a major in Engineering Physics.
Where I've Worked
AI Resident @ 1X Technologies
May - August 2025
1X is an AI and robotics company, with roots in Norway and Silicon Valley, dedicated to building fully autonomous humanoid robots that live and learn among us.
- Trained RL policies for dexterous manipulation on NEO hand V3, and added randomization for sim-to-real transfer
- Designed metrics to benchmark RL policies in both Isaac Gym and MuJoCo, evaluating sim-to-sim robustness
- Developed a ROS 2 Humble C++ controller to deploy evaluated policies in real‑time simulation and teleoperation
- Built Tkinter-based local and Streamlit-based browser app for object segmentation mask data collection using SAM2
- Integrated Cloudflare R2 and DBeaver SQL backend to load frames and store operator clicks on 1M+ frames
Some of my skills...
Featured Projects
Featured Project
MMOsaic: Combining Specialist Policies for Generalist Multi-Agent Play
Built as part of the Deep Reinforcement Learning Control course at CMU, this project developed a hierarchical multi-agent framework for Neural MMO. The system trains specialist policies (Combat, Forage, Survival) via distributed self-play using IMPALA and composes them into a generalist agent using a Mixture-of-Experts approach. We trained using PPO and UPGO, outperforming all baselines to achieve 2nd place.
- Python
- PyTorch
- IMPALA
- Distributed RL
- MARL
Featured Project
Bone.P.A.R.T.E
The project aims to address the limitations of Total Knee Arthroplasty by integrating AR with robot assisted manipulation, enhancing surgical visualization and procedural accuracy. The system provides functionality to overlay a surgical plan on the patient’s anatomy using the Apple Vision Pro headset, while a KUKA LBR MED7 robotic arm is used to screw surgical pins into bones with sub-centimeter precision (2mm and 2°).
- Python
- C++
- Swift
- ROS2
- MoveIT2
- SAM
- DinoV3
Featured Project
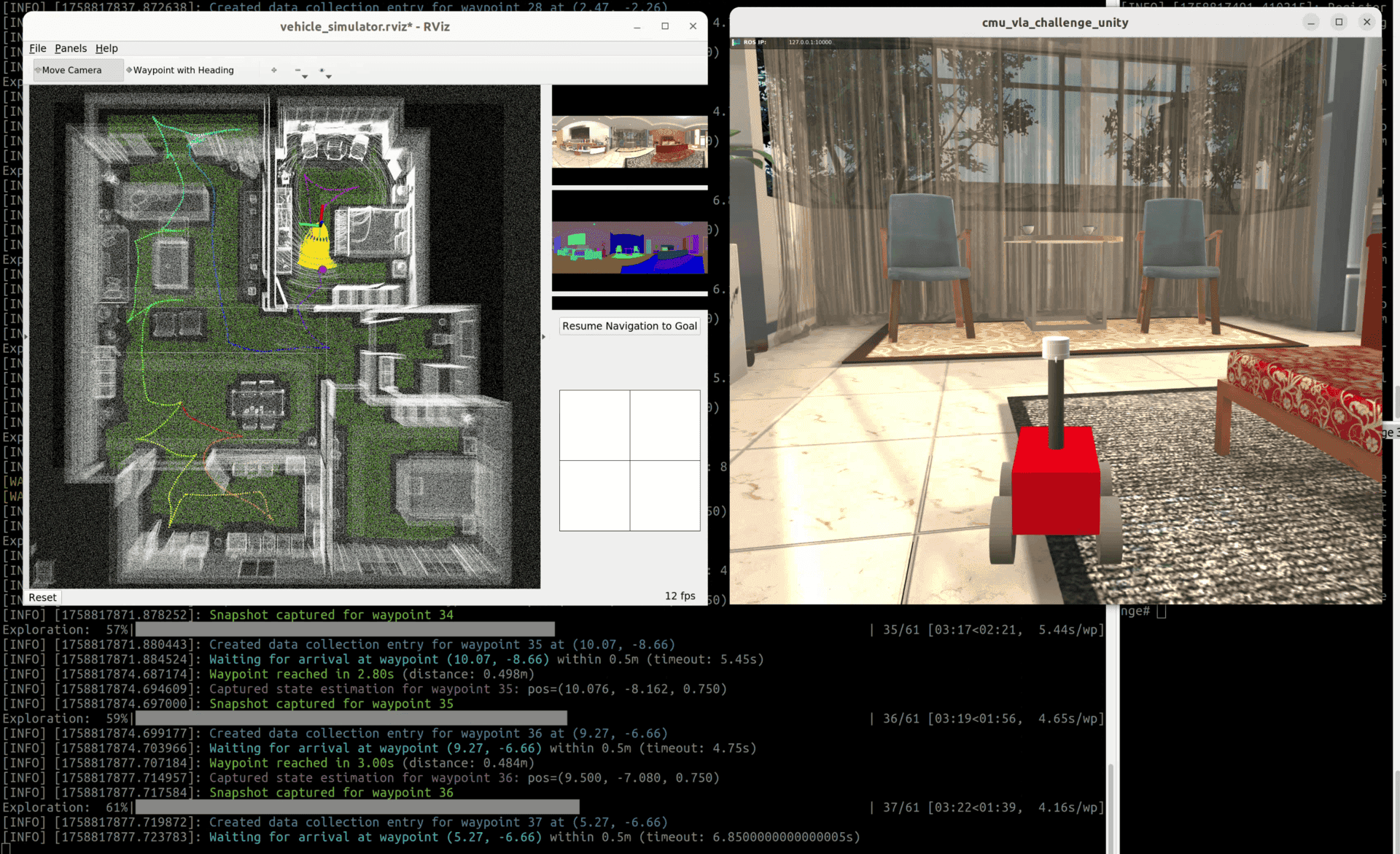
CMU Vision Language Autonomy Challenge
Built for the CMU Vision-Language-Autonomy Challenge (IROS 2025), this project developed a Vision-Language Navigation system combining Gemini 2.5 Pro's embodied reasoning with a custom ROS state machine. The system intelligently resolves spatial queries (e.g., "closest to the window") to produce object references and waypoint plans under a strict 10-minute limit. The entire stack was containerized via Docker for reliable deployment on real robot hardware, achieving 3rd place in the competition.
- Python
- ROS
- Gemini 2.5 Pro
- Docker
Featured Project
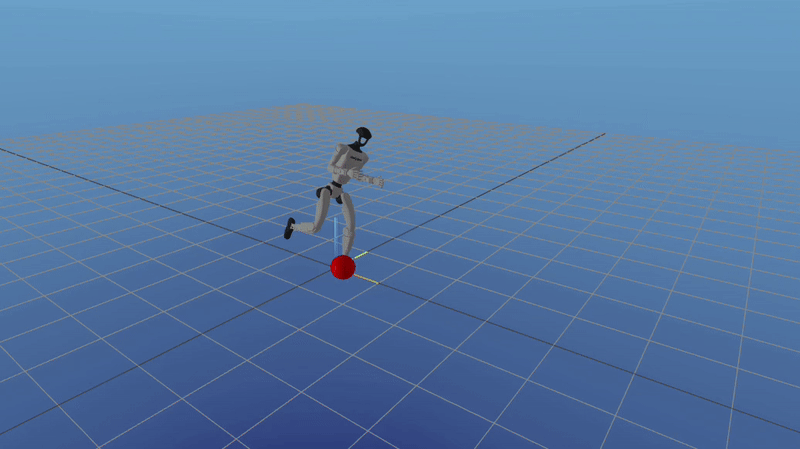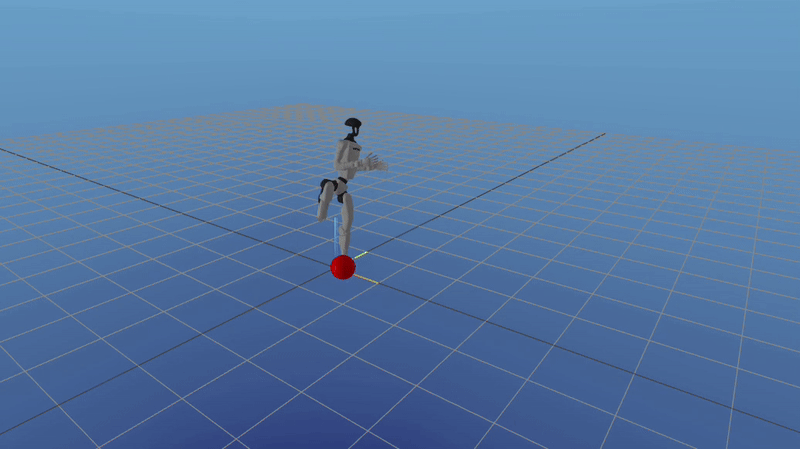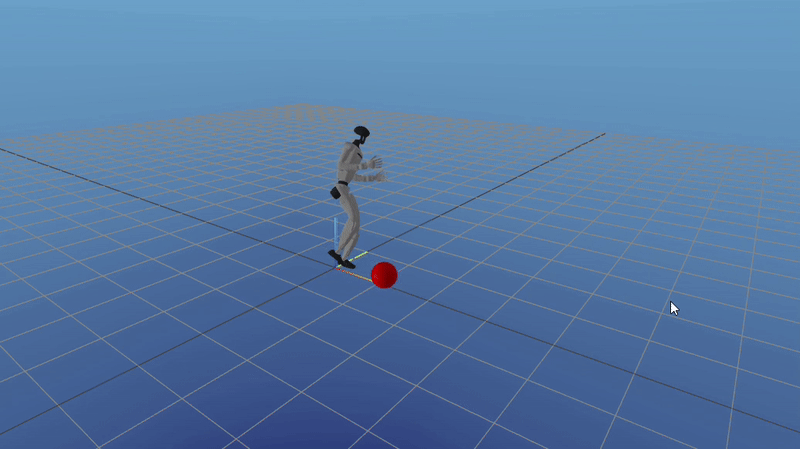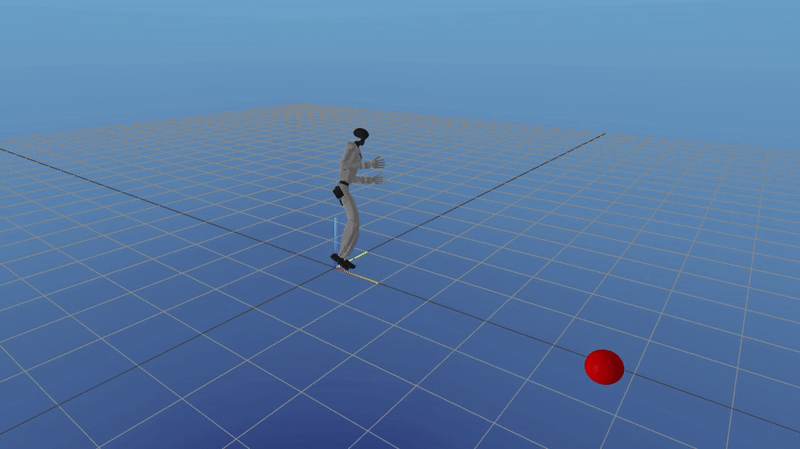
Unitree G1 Soccer Ball Kicking
Built as part of the Optimal Control and Reinforcement Learning course at CMU, this project simulated a penalty-style soccer kick using the Unitree G1 humanoid. The system computed the required impulse to strike the ball toward a target, generated a feasible motion with direct collocation, and used infinite-horizon LQR for balancing along with time-varying LQR for trajectory tracking.
- Julia
- IHLQR
- TVLQR
- QP
- DIRCOL
Featured Project
Stamp Pixel art using Franka arm
Built as part of the Robot Autonomy course at CMU, this project used a Franka Emika Panda arm with a stamping mechanism to autonomously generate pixel art. The system converts images into grid patterns, optimizes stamping order with Christofides’ algorithm to minimize travel, and uses force-controlled stamping with ArUco tagged ink pads for adaptability.
- ROS1
- Python
- FrankaPy
Publications
Robustifying a reinforcement learning agent-based bionic reflex controller through an adaptive sliding mode control
Robotica, Cambridge University Press • Nov. 2024
This study investigates the robustification of a reinforcement learning policy for implementing intelligent bionic reflex control, i.e., slip and deformation prevention of the grasped objects. RL-derived policies are vulnerable to failures in environments characterized by dynamic variability. To mitigate this vulnerability, we propose a methodology involving the incorporation of an adaptive sliding mode controller into a pre-trained RL policy.
Grasp Force Optimization as a Bilinear Matrix Inequality Problem: A Deep Learning Approach
6th National Conference on Multidisciplinary Design, Analysis and Optimization • Dec. 2023
Grasp force synthesis is a non-convex optimization problem involving constraints that are bilinear. The focus of this paper is to undertake a grasp analysis of biomimetic grasping in multi-fingered robotic hands as a bilinear matrix inequality (BMI) problem. Our analysis is to solve it using a deep learning approach to make the algorithm efficiently generate force closure grasps with optimal grasp quality on untrained/unseen objects.
Reinforcement Learning-Based Bionic Reflex Control for Anthropomorphic Robotic Grasping exploiting Domain Randomization
ArXiv Paper • Sep. 2023
In this study, we introduce an innovative bionic reflex control pipeline, leveraging reinforcement learning; eliminating the need for human intervention during control design. Our proposed bionic reflex controller has been designed and tested on an anthropomorphic hand, manipulating deformable objects in the PyBullet physics simulator, incorporating domain randomization for enhanced Sim2Real transferability.
Get In Touch
Whether you have a question or just want to say hi! My inbox is always open.
Say Hello